[ad_1]
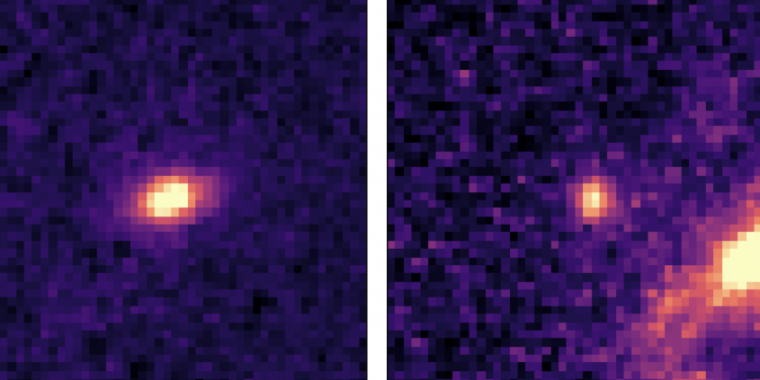
Enlarge / The 2 newly imaged galaxies, with the older one at proper.
One of many design objectives for the James Webb Area Telescope was to supply the flexibility to picture at wavelengths that may reveal the Universe’s first stars and galaxies. Now, only a few weeks after its first photos had been revealed, we’re getting a robust indication that it is a success. In a number of the knowledge NASA has made public, researchers have noticed as many as 5 galaxies from the distant Universe, already current only a few hundred million years after the Massive Bang. If confirmed to be as distant as they seem, considered one of them would be the most distant galaxy but noticed.
Opening up
For a lot of of its observatories, NASA permits astronomers to submit proposals for statement and permits these customers to have unique entry to the ensuing knowledge for a time afterward. However for its latest instrument, NASA has a set of targets the place the info shall be made public instantly, for anybody to research as they want. A few of these embody areas much like one of many first photos launched, the place a big cluster of galaxies within the foreground acts as a lens to amplify extra distant objects.
(You may have a look at the main points of one of many datasets used for this evaluation, referred to as GLASS, which used the cluster Abell 2744 to amplify distant objects, which had been urther magnified by the telescope.)
The pictures on this dataset had been lengthy exposures performed at totally different chunks of the infrared spectrum. The total vary of the wavelengths that the NIRCam instrument covers was divided up into seven chunks, and every chunk was imaged for anyplace from 1.5 to six.6 hours. A big worldwide staff of researchers used these chunks to carry out an evaluation that may assist them determine distant galaxies by searching for objects that had been current in some elements of the spectrum, however lacking from others.
Commercial
The search was based mostly on the understanding that many of the Universe was full of hydrogen atoms for a whole lot of tens of millions of years after the formation of the Cosmic Microwave Background. These would take in any gentle at or above a wavelength that was adequate to ionize the hydrogen, basically making the Universe opaque to those wavelengths. On the time, this cutoff was someplace within the UV finish of the spectrum. However in the mean time, the Universe’s growth shifted that cutoff into the infrared portion of the spectrum—one of many key causes that the Webb was designed to be delicate to those wavelengths.
First you do not see it (left), then you definately do. Reversed brightness photos present an object showing in a area of house highlighted by crosshairs, however solely at longer wavelengths.
So the staff regarded for objects that had been current within the photos of the bottom vitality chunks of the infrared spectrum imaged by Webb however absent from the higher-energy chunks. And the exact level at which it vanished signifies how red-shifted the cutoff is for that galaxy, and thus how distant the galaxy is. (You may count on future analysis to contain an analogous strategy.)
This technique produced 5 totally different objects of curiosity, and a draft manuscript focuses on the 2 most distant of those: GLASS-z13 and GLASS-z11. The previous is much more distant than the furthest confirmed distance of something noticed within the Hubble Deep Discipline; if confirmed, this could make it the furthest object we learn about and thus the closest in time to the Massive Bang.
[ad_2]