[ad_1]
It has been some time since I’ve posted to the weblog, however recently I’ve really been engaged on the UBR-1 once more after a considerably lengthy hiatus. In case you missed the sooner posts on this collection:
ROS2 Humble
The most recent ROS2 launch got here out just some weeks in the past. ROS2 Humble targets Ubuntu 22.04 and can also be a long run help (LTS) launch, which means that each the underlying Ubuntu working system and the ROS2 launch get a full 5 years of help.
Since putting in working methods on robots is usually a ache, I solely use the LTS releases and so I needed to migrate from the earlier LTS, ROS2 Cunning (on Ubuntu 20.04). General, there aren’t many adjustments to the low-level ROS2 APIs as issues are getting extra secure and mature. For some larger stage packages, corresponding to MoveIt2 and Navigation2, the story is a bit totally different.
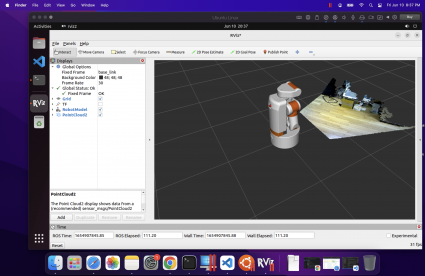
Visualization
One of many good issues in regards to the ROS2 Cunning launch was that it focused the identical working system as the ultimate ROS1 launch, Noetic. This allowed customers to have each ROS1 and ROS2 put in side-by-side. If you happen to’re nonetheless creating in ROS1, which means you in all probability don’t wish to improve all of your computer systems fairly but. Whereas my robotic now runs Ubuntu 22.04, my desktop remains to be working 18.04.
Due to this fact, I needed to discover a technique to visualize ROS2 information on a pc that didn’t have the most recent ROS2 put in. Initially I attempted the Foxglove Studio, however didn’t have any luck with issues really connecting utilizing the native ROS2 interface (the rosbridge-based interface did work). Foxglove is actually attention-grabbing, however up to now it’s probably not an RVIZ alternative – they seem like extra centered on offline information visualization.
I then moved onto working rviz2 inside a docker surroundings – which works nicely when utilizing the rocker software:
sudo apt-get set up python3-rockersudo rocker –net=host –x11 osrf/ros:humble-desktop rviz2
In case you are utilizing an NVIDIA card, you’ll want so as to add –nvidia together with –x11.
With a purpose to correctly visualize and work together with my UBR-1 robotic, I wanted so as to add the ubr1_description package deal to my workspace as a way to get the meshes and in addition my rviz configurations. To perform this, I wanted to create my very own docker picture. I largely primarily based it off the underlying ROS docker photographs:
ARG WORKSPACE=/choose/workspace
FROM osrf/ros:humble-desktop
# set up construct toolsRUN apt-get replace && apt-get set up -q -y –no-install-recommends python3-colcon-common-extensions git-core && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# get ubr codeARG WORKSPACEWORKDIR $WORKSPACE/srcRUN git clone https://github.com/mikeferguson/ubr_reloaded.git && contact ubr_reloaded/ubr1_bringup/COLCON_IGNORE && contact ubr_reloaded/ubr1_calibration/COLCON_IGNORE && contact ubr_reloaded/ubr1_gazebo/COLCON_IGNORE && contact ubr_reloaded/ubr1_moveit/COLCON_IGNORE && contact ubr_reloaded/ubr1_navigation/COLCON_IGNORE && contact ubr_reloaded/ubr_msgs/COLCON_IGNORE && contact ubr_reloaded/ubr_teleop/COLCON_IGNORE
# set up dependenciesARG WORKSPACEWORKDIR $WORKSPACERUN . /choose/ros/$ROS_DISTRO/setup.sh && apt-get replace && rosdep set up -q -y –from-paths src –ignore-src && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# construct ubr codeARG WORKSPACEWORKDIR $WORKSPACERUN . /choose/ros/$ROS_DISTRO/setup.sh && colcon construct
# setup entrypointCOPY ./ros_entrypoint.sh /
ENTRYPOINT [“/ros_entrypoint.sh”]CMD [“bash”]
The picture derives from humble-desktop after which provides the construct instruments and clones my repository. I then ignore nearly all of packages, set up dependencies after which construct the workspace. The ros_entrypoint.sh script handles sourcing the workspace configuration.
#!/bin/bashset -e
# setup ros2 environmentsource “/choose/workspace/set up/setup.bash”exec “$@”
I might then create the docker picture and run rviz inside it:
docker construct -t ubr:mainsudo rocker –net=host –x11 ubr:foremost rviz2
The complete supply of those docker configs is within the docker folder of my ubr_reloaded repository. NOTE: The up to date code within the repository additionally provides a late-breaking change to make use of CycloneDDS as I’ve had quite a few connectivity points with FastDDS that I’ve not been capable of debug.
Visualization on MacOSX
I additionally regularly need to have the ability to work together with my robotic from my Macbook. Whereas I beforehand put in ROS2 Cunning on my Intel-based Macbook, the scenario is sort of modified now with MacOSX being downgraded to Tier 3 help and the brand new Apple M1 silicon (and Apple’s numerous different locking mechanisms) making it tougher and tougher to setup ROS2 straight on the Macbook.
As with the Linux desktop, I attempted out Foxglove – nevertheless it’s a bit restricted on Mac. The MacOSX surroundings doesn’t enable opening the required ports, so the direct ROS2 subject streaming doesn’t work and you need to use rosbridge. I discovered I used to be capable of visualize sure matters, however that switching between matters regularly broke.
At this level, I used to be about to surrender, till I seen that Ubuntu 22.04 arm64 is a Tier 1 platform for ROS2 Humble. I proceeded to put in the arm64 model of Ubuntu inside Parallels (Observe: I used to be low-cost and initially tried to make use of the VMWare know-how preview, however was unable to get the installer to even boot). There are a number of methods right here as there is no such thing as a arm64 desktop installer, so you need to set up the server version after which improve it to a desktop. There’s a detailed description of this workflow on askubuntu.com. Putting in ros-humble-desktop from arm64 Debians was completely straightforward.
rviz2 runs comparatively fast contained in the Parallels VM, however total it was not fairly as fast or secure as utilizing rocker on Ubuntu. Nonetheless, it’s very nice to have the ability to do some ROS2 growth when touring with solely my Macbook.
Migration Notes
Observe: every of the hyperlinks on this part is to a commit or PR that implements the mentioned adjustments.
Within the core ROS API, there are solely a handful of adjustments – and most of them are literally merely fixing potential bugs. The logging macros have been up to date for safety functions and require c-strings just like the previous ROS1 macros did. Moreover the macros at the moment are higher at detecting invalid substitution strings. Ament has additionally gotten higher at detecting lacking dependencies. The updates I made to robot_controllers present simply what number of bugs had been caught by this extra strict checking.
image_pipeline has had some minor updates since Cunning, primarily to enhance consistency between plugins and so I wanted to replace some subject remappings.
Navigation has essentially the most updates. amcl mannequin sort names have been modified for the reason that fashions at the moment are plugins. The API of costmap layers has modified considerably, and so a variety of updates had been required simply to get the system began. I then made a extra detailed move by means of the documentation and located a number of extra points and enhancements with my config, particularly across the conduct tree configuration.
I additionally determined to do a correct port of graceful_controller to ROS2, ranging from the most recent ROS1 code since a variety of enhancements have occurred previously 12 months since I had initially ported to ROS2.
Subsequent steps
There are nonetheless a variety of new options to discover with Navigation2, however my rapid focus goes to shift in the direction of getting MoveIt2 setup on the robotic, since I can’t simply swap between ROS1 and ROS2 anymore after upgrading the working system.
Michael Ferguson
[ad_2]