[ad_1]
By Marco Arruda
On this put up you’ll learn to publish to a ROS2 matter utilizing ROS2 C++. As much as the tip of the video, we’re shifting the robotic Dolly robotic, simulated utilizing Gazebo 11.
You’ll be taught:
Learn how to create a node with ROS2 and C++
Learn how to public to a subject with ROS2 and C++
1 – Setup atmosphere – Launch simulation
Earlier than the rest, ensure you have the rosject from the earlier put up, you’ll be able to copy it from right here.
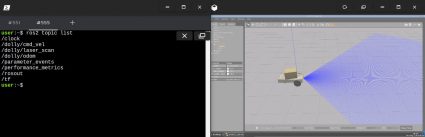
Launch the simulation in a single webshell and in a special tab, checkout the matters we now have accessible. It’s essential to get one thing just like the picture under:
2 – Create a subject writer
Create a brand new file to container the writer node: moving_robot.cpp and paste the next content material:
#embody <chrono>
#embody <useful>
#embody <reminiscence>
#embody “rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp”
#embody “geometry_msgs/msg/twist.hpp”
utilizing namespace std::chrono_literals;
/* This instance creates a subclass of Node and makes use of std::bind() to register a
* member perform as a callback from the timer. */
class MovingRobot : public rclcpp::Node {
public:
MovingRobot() : Node(“moving_robot”), count_(0) {
publisher_ =
this->create_publisher(“/dolly/cmd_vel”, 10);
timer_ = this->create_wall_timer(
500ms, std::bind(&MovingRobot::timer_callback, this));
}
non-public:
void timer_callback() {
auto message = geometry_msgs::msg::Twist();
message.linear.x = 0.5;
message.angular.z = 0.3;
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), “Publishing: ‘%f.2’ and %f.2”,
message.linear.x, message.angular.z);
publisher_->publish(message);
}
rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr timer_;
rclcpp::Writer::SharedPtr publisher_;
size_t count_;
};
int most important(int argc, char *argv[]) {
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
rclcpp::spin(std::make_shared());
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}QoS (High quality of Service)
Just like the subscriber it’s created a category that inherits Node. A publisher_ is setup and in addition a callback, though this time isn’t a callback that receives messages, however a timer_callback known as in a frequency outlined by the timer_ variable. This callback is used to publish messages to the robotic.
The create_publisher methodology wants two arguments:
matter identify
QoS (High quality of Service) – That is the coverage of information saved within the queue. You may make use of various middlewares and even use some offered by default. We’re simply establishing a queue of 10. By default, it retains the final 10 messages despatched to the subject.
The message revealed should be created utilizing the category imported:
message = geometry_msgs::msg::Twist();
We make sure the callback strategies on the subscribers aspect will all the time acknowledge the message. That is the way in which it needs to be revealed by utilizing the writer methodology publish.
3 – Compile and run the node
To be able to compile we have to alter some issues within the ~/ros2_ws/src/my_package/CMakeLists.txt. So add the next to the file:
Add the geometry_msgs dependency
Append the executable moving_robot
Add set up instruction for moving_robot
find_package(geometry_msgs REQUIRED)
…
# shifting robotic
add_executable(moving_robot src/moving_robot.cpp)
ament_target_dependencies(moving_robot rclcpp geometry_msgs)
…
set up(TARGETS
moving_robot
reading_laser
DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME}/
)
We will run the node like under:
supply ~/ros2_ws/set up/setup.bashros2 run my_package
Associated programs & additional hyperlinks:
The put up Exploring ROS2 utilizing wheeled Robotic – #3 – Transferring the Robotic appeared first on The Assemble.
The Assemble Weblog
[ad_2]