[ad_1]
Discovering methods to attach the human physique to expertise might have broad purposes in well being and leisure. A brand new “electrical plastic” might make self-powered wearables, real-time neural interfaces, and medical implants that merge with our our bodies a actuality.
Whereas there was vital progress within the growth of wearable and implantable expertise lately, most digital supplies are arduous, inflexible, and have poisonous metals. A wide range of approaches for creating “comfortable electronics” has emerged, however discovering ones which might be sturdy, power-efficient, and simple to fabricate is a major problem.
Natural ferroelectric supplies are promising as a result of they exhibit spontaneous polarization, which implies they’ve a secure electrical area pointing in a selected route. This polarization might be flipped by making use of an exterior electrical area, permitting them to operate like a bit in a traditional pc.
Essentially the most profitable comfortable ferroelectric is a cloth referred to as polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), which has been utilized in business merchandise like wearable sensors, medical imaging, underwater navigation gadgets, and comfortable robots. However PVDF’s electrical properties can break down when uncovered to greater temperatures, and it requires excessive voltages to flip its polarization.
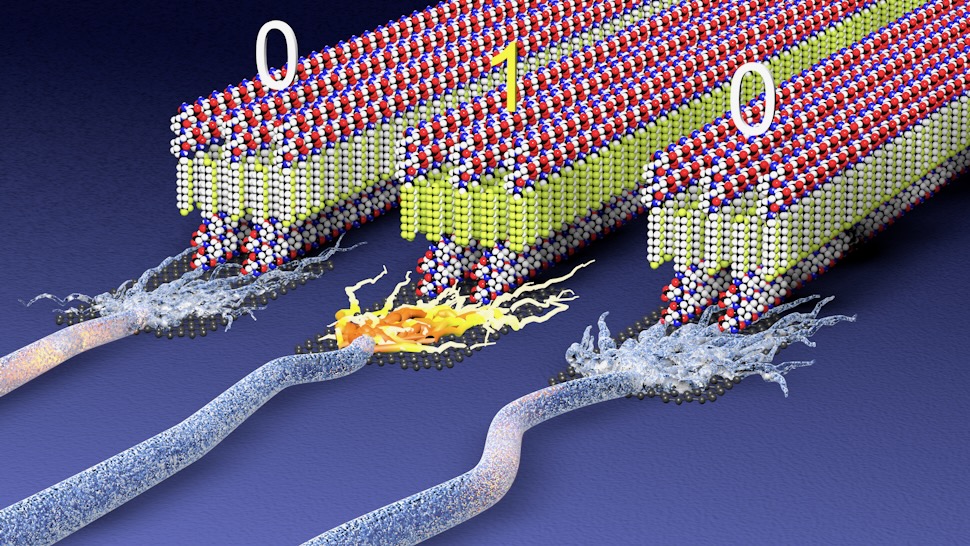
Now, in a paper printed in Nature, researchers at Northwestern College have proven that combining the fabric with quick chains of amino acids generally known as peptides can dramatically cut back energy necessities and enhance warmth tolerance. And the incorporation of biomolecules into the fabric opens the prospect of immediately interfacing electronics with the physique.
To create their new “electrical plastic” the group used a kind of molecule generally known as a peptide amphiphile. These molecules characteristic a water-repelling element that helps them self-assemble into advanced constructions. The researchers related these peptides to quick strands of PVDF and uncovered them to water, inflicting the peptides to cluster collectively.
This made the strands coalesce into lengthy, versatile ribbons. In testing, the group discovered the fabric might face up to temperatures of 110 levels Celsius, which is roughly 40 levels greater than earlier PVDF supplies. Switching the fabric’s polarization additionally required considerably decrease voltages, regardless of being made up of 49 % peptides by weight.
The researchers informed Science that in addition to having the ability to retailer vitality or info within the materials’s polarization, it’s additionally biocompatible. This implies it might be utilized in all the pieces from wearable gadgets that monitor very important indicators to versatile implants that may change pacemakers. The peptides is also related to proteins inside cells to file organic exercise and even stimulate it.
One problem is that though PVDF is biocompatible, it will probably break down into so-called “without end chemical compounds,” which stay within the atmosphere for hundreds of years and research have linked to well being and environmental issues. A number of different chemical compounds the researchers used to manufacture their materials additionally fall into this class.
“This advance has enabled a variety of engaging properties in comparison with different natural polymers,” Frank Leibfarth, of UNC Chapel Hill, informed Science. However he identified that the researchers had solely examined very small quantities of the molecule, and it’s unclear how simple will probably be to scale them up.
If the researchers can prolong the strategy to bigger scales, nonetheless, it might deliver a number of thrilling new potentialities on the interface between our our bodies and expertise.
Picture Credit score: Mark Seniw/Heart for Regenerative Nanomedicine/Northwestern College
[ad_2]