[ad_1]
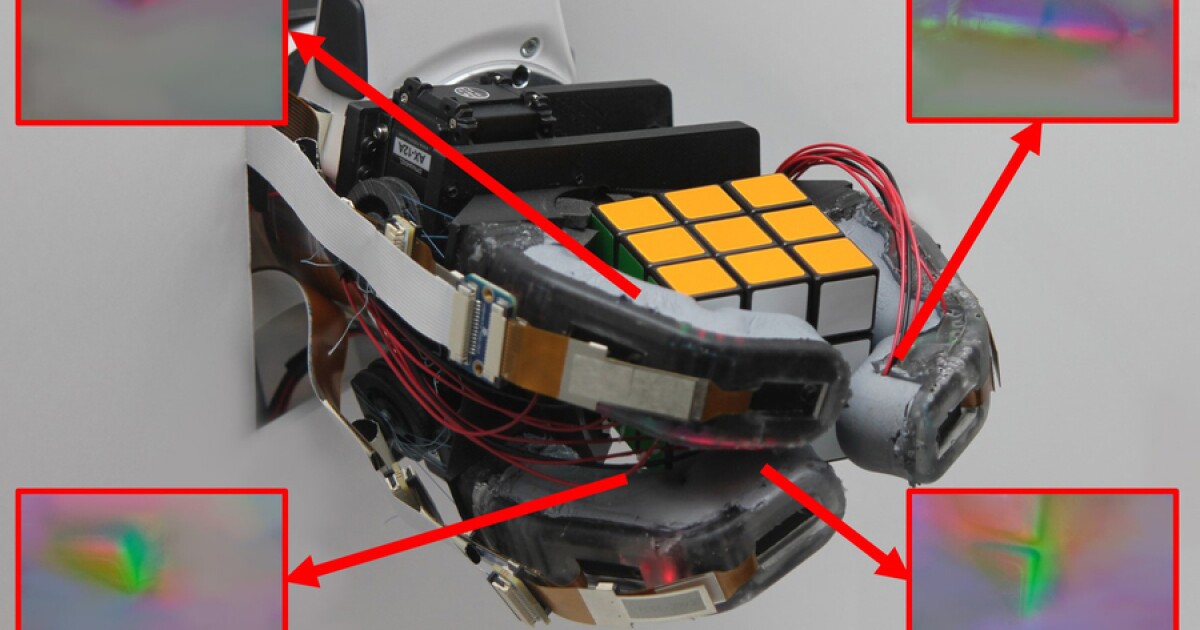
If a robotic goes to be greedy delicate objects, then that bot had higher know what these objects are, so it might deal with them accordingly. A brand new robotic hand permits it to take action, by sensing the form of the thing alongside the size of its three digits.Developed by a workforce of scientists at MIT, the experimental gadget is called the GelSight EndoFlex. And true to its title, it incorporates the college’s GelSight expertise, which had beforehand solely been utilized within the fingertip pads of robotic arms.The EndoFlex’s three mechanical digits are organized in a Y form – there are two “fingers” on the high, with an opposable “thumb” on the backside. Each consists of an articulated onerous polymer skeleton, encased inside a comfortable and versatile outer layer. The GelSight sensors themselves – two per digit – are situated on the underside of the highest and center sections of these digits.Every sensor incorporates a slab of clear, artificial rubber that’s coated on one facet with a layer of metallic paint – that paint serves because the finger’s pores and skin. When the paint is pressed in opposition to a floor, it deforms to the form of that floor. Wanting by means of the other, unpainted facet of the rubber, a tiny built-in digicam (with assist from three coloured LEDs) can picture the minute contours of the floor, urgent up into the paint.Particular algorithms on a linked pc flip these contours into 3D photos which seize particulars lower than one micrometer in depth and roughly two micrometers in width. The paint is important in an effort to standardize the optical qualities of the floor, in order that the system is not confused by a number of colours or supplies.Within the case of the EndoFlex, by combining photos from six such sensors directly (two on every of the three digits), it is doable to create a three-dimensional mannequin of the merchandise being grasped. Machine-learning-based software program is then in a position to determine what object that mannequin represents, after the hand has grasped the thing only one time. The system has an accuracy fee of about 85% in its current kind, though that quantity ought to enhance because the expertise is developed additional.”Having each comfortable and inflexible parts is essential in any hand, however so is with the ability to carry out nice sensing over a extremely massive space, particularly if we need to take into account doing very difficult manipulation duties like what our personal arms can do,” mentioned mechanical engineering graduate scholar Sandra Liu, who co-led the analysis together with undergraduate scholar Leonardo Zamora Yañez and Prof. Edward Adelson.”Our aim with this work was to mix all of the issues that make our human arms so good right into a robotic finger that may do duties different robotic fingers can’t presently do.”Supply: MIT
[ad_2]
Sign in
Welcome! Log into your account
Forgot your password? Get help
Privacy Policy
Password recovery
Recover your password
A password will be e-mailed to you.