[ad_1]

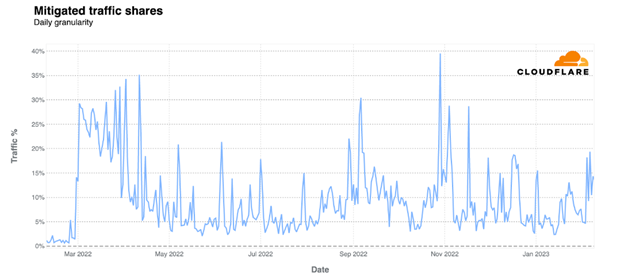
When Russia invaded Ukraine on Feb. 24, 2022, a lot dialogue ensued about how the struggle can be each cyber and kinetic. A yr later, the consensus appears to be that whereas there was plenty of cyberattack exercise, it wasn’t as harmful as many had feared. That was partly as a consequence of numerous governments and safety firms serving to to determine and block assaults.Between February 2022 and February 2023, a mean of 10% of all on-line site visitors to Ukraine was mitigations of potential assaults, Cloudflare mentioned in its evaluation of the Russian invasion’s influence on theUkrainian Web. Cloudflare protected Ukrainian Net purposes by filtering and monitoring HTTP site visitors to dam malicious assaults, together with distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) assaults.On Oct. 29, DDoS assault site visitors constituted 39% of whole site visitors to Cloudflare’s Ukrainian clients.The corporate shared a graph exhibiting the day by day proportion of software layer site visitors to Ukraine that Cloudflare mitigated as potential assaults utilizing its Net software firewall (WAF). In early March, 30% of all site visitors was mitigated. After a reasonably quiet summer season, assault exercise ticked again up in early September, in the course of the Ukrainian counteroffensive in east and south Ukraine.Extra particularly, 14% of whole site visitors from Ukraine was mitigated as potential assaults, whereas 10% of whole site visitors to Ukraine was mitigated as potential assaults up to now 12 months.Mitigated application-layer threats blocked by Cloudflare’s WAF have been 105% greater on Monday, Feb. 28, 2022 — 4 days after the invasion — in contrast with the Monday earlier than, Feb. 21, 2022. By March 8, that determine was 1,300%.What Got here Out of ‘Shields Up’In anticipation of Russian cyberattacks in opposition to Ukrainian targets and in opposition to organizations in international locations allied with Ukraine, the US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Safety Company (CISA) urged organizations to share info that might assist mitigate threats. “Each group — massive and small — should be ready to reply to disruptive cyber incidents,” CISA mentioned.Whereas sharing risk intelligence indubitably helped, the character of the assaults have been additionally much less subtle or harmful than feared.Cisco Talos researchers have been monitoring important infrastructure clients to determine threats and remediate assaults. Whereas there have been plenty of issues about harmful malware, what Talos is seeing — and blocking — plenty of is credentials harvesting, says Nick Biasini, Cisco Talos’ head of outreach. Attackers usually are not resorting to extremely subtle techniques however fairly are using mundane and recognizable strategies to attempt to achieve entry to networks and accounts, he says.Affect on Important InfrastructureCloudflare’s evaluation of Ukraine’s Web site visitors exhibits peaks and drops in utilization corresponding with army exercise. For instance, town of Chernihiv had a big drop in site visitors the primary week of the struggle and residual site visitors by mid-March, with site visitors selecting up after the Russian retreat in early April, Cloudflare famous. Within the fall, Russian army items began focusing on Ukrainian important infrastructure, inflicting widespread energy outages and Web blackouts. A few of these strikes brought about as a lot as a 50% lower in Web site visitors, in accordance with Cloudflare’s evaluation. The disruptions usually lasted solely a day or two, “additional emphasizing the continued influence of the battle on Ukraine’s infrastructure,” Cloudflare famous.”All through the remainder of the yr and into 2023, Ukraine has continued to face intermittent Web disruptions,” Cloudflare additionally wrote.Ripple Results Across the WorldSecurity leaders in East Asia are rigorously watching how the struggle between Russia and Ukraine unfolds, as plenty of the geopolitical tensions and rhetoric are much like the long-simmering state of affairs between China and Taiwan. Organizations are “questioning what sort of disruptive assaults to anticipate” and the way the struggle in Ukraine may have an effect on the Taiwan state of affairs, says Mihoko Matsubara, chief cybersecurity strategist at NTT. There has already been some exercise, though it has been of the “cyber nuisance” selection, fairly than destruction, Matsubara says. East Asian firms are already seeing DDoS assaults, defacements, and disinformation campaigns, she says.Matsubara was cautious to not downplay the seriousness of the assaults, as they’re nonetheless disruptive to organizations. NTT has additionally seen some wiper assaults used to disrupt humanitarian assist efforts, which can be a harbinger of actions to return.Unhealthy Actors Get PoliticalCybercriminals have been expressing their very own opinions — and political allegiances — in regards to the struggle. For instance, Coalition’s newest “Cyber Risk Index” report dug into assaults in opposition to databases uncovered to the Web. Coalition noticed a complete 264,408 IP addresses operating MongoDB cases in 2022, and 68,423 of them — or 26% — have been compromised. Coalition discovered a handful of compromised MongoDB servers the place the attackers renamed the databases to SLAVA_UKRAINI, or “Glory to Ukraine!””Risk actor exercise is commonly formed by fluctuations in financial situations,” famous the crew from Kroll’s Cyber Danger apply within the newest “Risk Panorama” report. “Because of the continued market volatility throughout the globe and the continued struggle on Ukraine, it’s probably that the unstable circumstances through which attackers thrive will persist in 2023.”
[ad_2]
Sign in
Welcome! Log into your account
Forgot your password? Get help
Privacy Policy
Password recovery
Recover your password
A password will be e-mailed to you.